What is your first visual when you hear about a test manager? A manager overseeing the testing of a process, viz. a website, app, or software? Well, if that’s what flashed through your mind at the first go, then you are almost there. True, as a starter, a test manager is responsible for every QC and monitoring of a testing process until the software is successfully rolled out.
However, isn’t that a very cliche definition? What different are we talking about here then? A test manager conducts a spectrum of roles beyond the obvious one. Let’s take a good look at such before your business chooses to hire the right test manager for your most crucial software.
Table of ContentsSuppose you are confused within a dichotomy of understanding what the main role of a test manager is or what a test manager does, what test management is, and what all fall under the purview of his/her functionalities. In that case, you certainly have landed on the right page.
Most test managers hail from the software engineering or quality control fields. They may have hands-on experience with testing teams and are familiar with various testing approaches, tools, & best practices. Managers of testing teams often have advanced degrees in computer science and a related subject and specific testing software or project management credentials.
A test manager’s income might be affected by their geographical location, level of expertise, and industry. Recent findings from Glassdoor indicate that the typical US test supervisor’s income is around $101,000 annually.
How different is a Software Test Manager?
A software test manager is responsible for keeping the testing group inspired, actively involved, and cooperatively working toward the project’s objectives. From handling the planning phase to the execution phase, the end-to-end process falls under the purview of a responsible and adept test manager.
An expert test manager is answerable for staying current on testing-related tools, technologies, & best practices to guarantee a trustworthy and effective procedure. Participating in business forums & conferences and receiving education and training comes under the purview of test management. These help you stay abreast of industry trends & updated with new technology.
Test Management describes the overall procedure of managing a software development project’s test efforts. Test case management is essential since it guarantees that the final software product will be of excellent craftsmanship and free of bugs.
So, what is the need of the test manager? The width of the responsibilities is pretty wide.
1. Organization and forethought: Zealous testing managers are accountable for coordinating and strategizing the project’s testing efforts. So, what does a test manager do? Creating tests in which test plans and test strategies serve the project’s larger purpose is a part of this.
2. Assuring High Standards: Adroit test managers must guarantee they follow all quality criteria. This aids in making sure the final software product is up to snuff for its intended audience.
3. Controlling danger: Managers of testing efforts must be alert to and able to mitigate any threats that may arise during the testing process. Hazards to the testing phase can be mitigated, & the project can be completed on schedule and within budget.
4. Leadership in a team: Managers of testing operations oversee the activities of the testing group. The process also involves establishing goals, communicating them to team members, & assessing their progress toward them.
5. Communication : Testing supervisors must update upper-level stakeholders on testing progress. This aids in making sure that all parties involved in the testing process comprehend what was done and why.
The test manager’s length and breadth of tasks and duties are ever-expanding and might change from one software needs to another. They cannot work in silos to phase out a software testing delivery. Collaborating with Auditor, System developer, External vendor, End User, QA Engineer, System Engineer, Testing Engineer, and more is an inevitable part of his/her functions.
But here are some of the more customary tasks of a test manager :
To sum up, a test manager is crucial to the success of any software project, as their work is directly tied to the final product’s quality, timeliness, and cost.
Despite every attempt to conduct quick testing, the process can often be mundane, slow, and inefficient.
A Test Manager is accountable for creating and executing thorough test strategies and plans that align with the project’s needs. More so, they create testing plans, assess which cases need to be tested, and create test cases.
1. Test Planning and Strategy Development
As a Test Manager, you must manage available resources. They need to make smart choices about distributing resources like testers, tools, & infrastructure to ensure the team can do its work effectively. Managers of testing operations often act as coaches and advisors to their teams.
2. Resource Management
During the phase known as “Test Execution and Reporting,” you’ll supervise the testing process to ensure everything goes off without a hitch. Additionally, responsible managers of testing efforts must ensure that participants receive timely and accurate reports on test outcomes.
3. Test Execution and Reporting
Another important function of a Test Manager is maintaining open lines of communication and managing stakeholders.
4. Stakeholder Management and Communication
Effective interaction are essential for managing stakeholders in Test Management since it keeps everyone abreast of the procedure for testing and its progress. The test manager should establish and maintain communication channels between the business shareholders, testers, developers, and management.
Furthermore, stakeholders should be kept up-to-date on the status of testing operations & any problems or concerns via regular reports & updates.
5. Risk Management
Test Managers must be aware of any threats to the procedure for testing or the final product’s quality to manage the associated risks effectively. To deal with the risks that may arise, they need to create a risk management strategy & a risk mitigation plan.
6. QA and QC
Two essential components of Test Management are quality assurance (QA) & quality control (QC). QA focuses on defect prevention by building procedures and processes to ensure the software is built to high-quality standards. Besides, quality control aims to find errors and fix them before releasing the program to the public. Indeed, the application’s quality depends on the Test Managers’ ability to set explicit QA and QC methods and criteria.
7. Process Improvement
Process improvement is integral to the Test Management methodology. On top of that, methods for better testing can be developed and implemented once an analysis of the current state of testing has been conducted. In addition, test managers ought to examine the outcomes of efforts to improve processes regularly to ensure they are working.
The achievement of testing activities depends on the Test Manager’s possessing the following abilities and skills:
1. Technical Skills
The ideal candidate for the role of Test Manager will have a strong grasp of testing processes, test automation, & software. The managers need to be experts at developing test strategies, test cases, evaluating scripts, and putting them to use. Also, they should have a solid foundation in the SDLC and standard assurance practices.
2. Adaptability and Flexibility
An important attribute of a Test Manager is versatility. The professional should be an expert in adjusting to shifting priorities & deadlines. The ability to adapt testing tactics & plans to new situations and perform efficiently in a fast-paced setting is essential.
Whether modifying an existing process, agreeing to a plan, assessing quality checks, or improving test efforts, a test manager efficiently takes care of every process. They also need to pick up gadgets and software programs rapidly.
Now, considering the vast plethora of roles test managers can manage, do you think it’s a cakewalk to execute the entire process? Well, no!
There are an array of obstacles that a Test Manager could encounter while carrying out tests. Let’s sneak a peek into some examples of such difficulties:
1. Time and Resource Constraints
Managing the testing procedure in a short period, along with a crunch in resources, is a major problem for Test Managers. This involves taking charge of the testing schedule, assigning resources wisely, and keeping testing tasks on track to ensure they are done on time.
2. Complexity of Applications
Without a doubt, testing becomes increasingly difficult as application complexity increases. Test managers are responsible for equipping their teams with the knowledge and resources to test sophisticated software successfully.
3. Changing Technology Landscape
Keeping testing procedures up-to-date necessitates that Test Managers brace the emerging technologies and the most cutting-edge testing tools. To ace the competition, they must be ready to incorporate cutting-edge tools into their testing framework.
4. Team Management and Motivation
Test managers are responsible for leading their teams to success by keeping them inspired and productive. This entails listening to others, resolving disagreements, and encouraging teamwork.
5. Balancing Quality with Business Needs
Managers of testing efforts must balance strict attention to detail and the company’s practical needs. Determining how much testing is needed depends on the importance of the app & the resources that are accessible.
To guarantee that testing procedures are efficient, effective, & yield high-quality findings, Test Managers need to be able to surmount these obstacles.
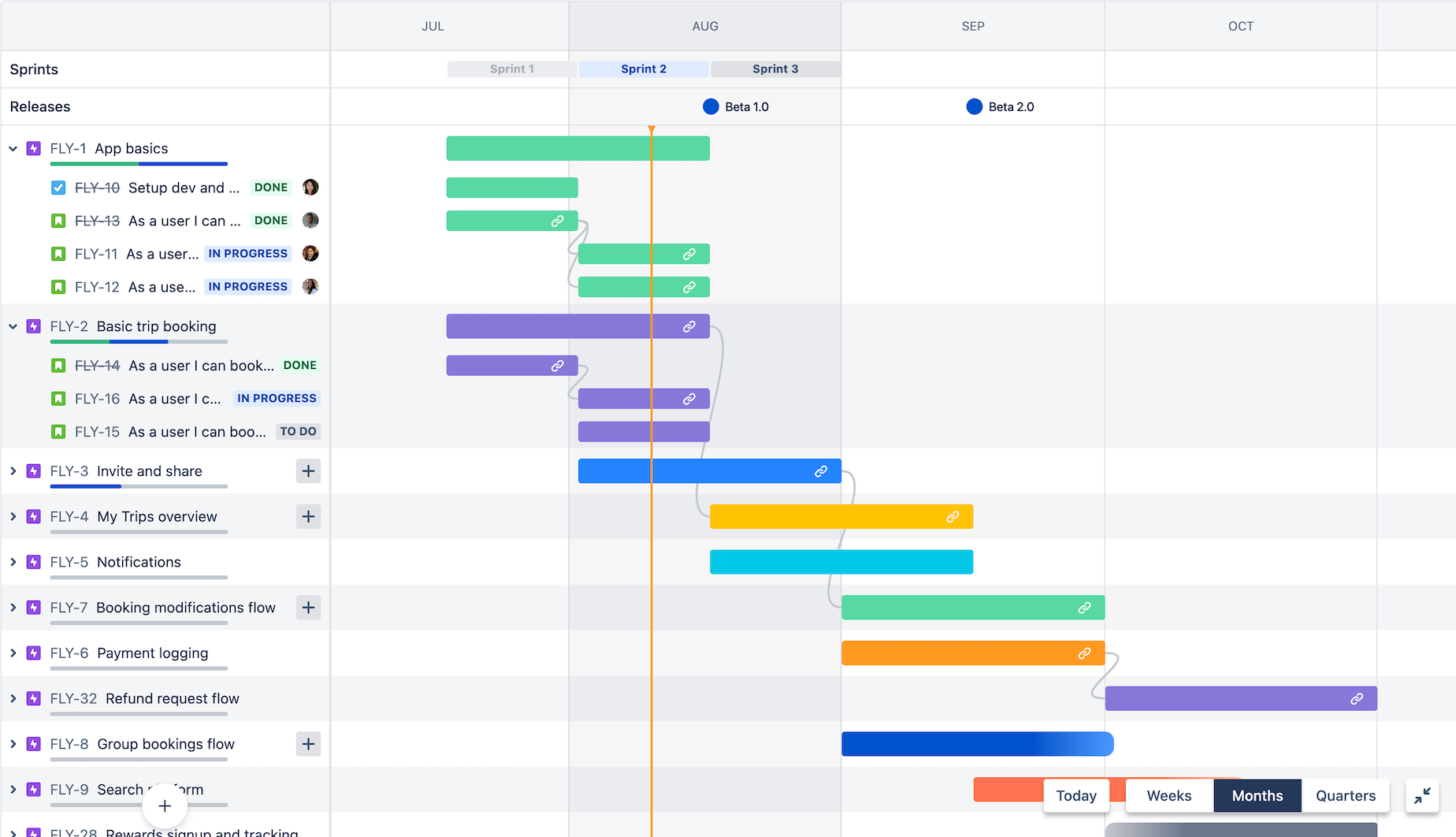
JIRA
In Agile software development, JIRA deserves special mention as a Test Management Tool. Its primary functions are project management, bug tracking, and test case administration. JIRA is an effective Test Management solution because of its compatibility with other programs.

Cloud-based testing is also becoming increasingly popular, providing teams greater flexibility and scalability. Teams can quickly and easily set up and tear down testing environments as needed, reducing the time and resources required for testing.
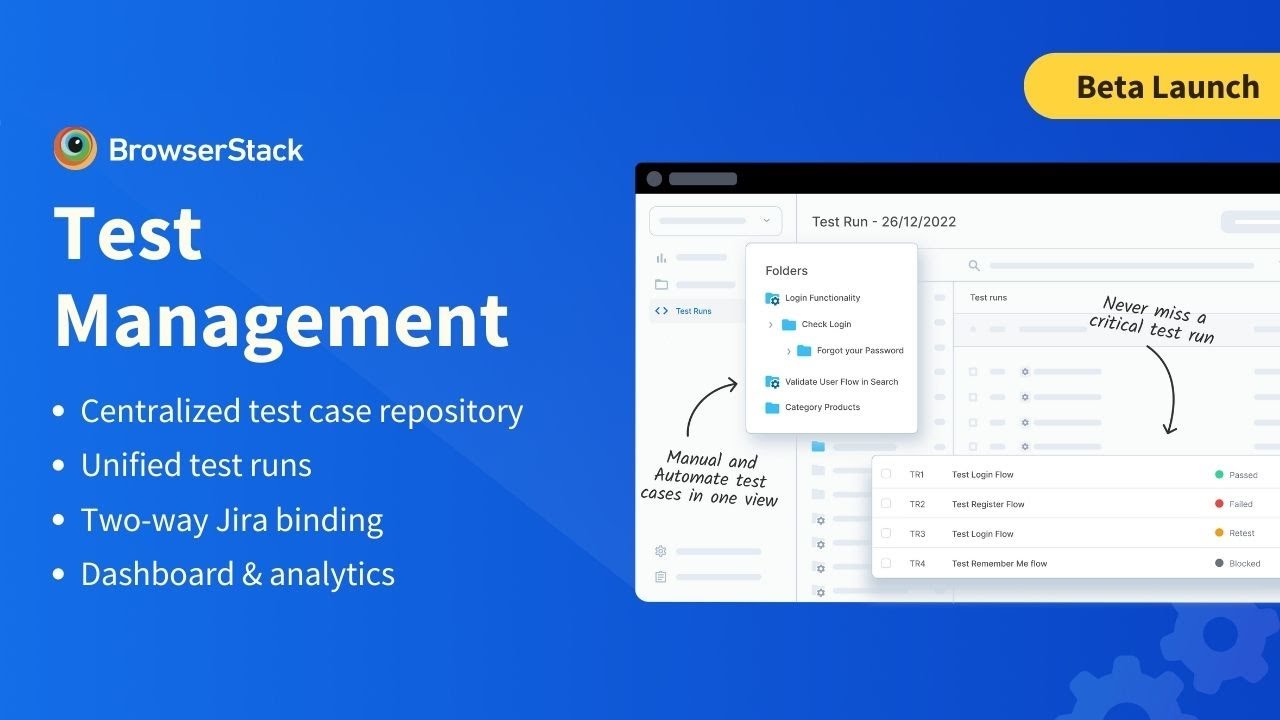
BrowserStack Test Management offers a comprehensive solution for efficient testing efforts. Create, manage, and track manual & automated test cases with integrated workflows and dashboards for real-time insights into software quality. Leverage insights on testing trends to ship high-quality products faster.
Here we go with the scope of a test manager’s roles. Test Managers may guarantee the success of their testing efforts by fostering communication and cooperation, creating evaluation procedures and standards, adopting test automation & integration, supporting continuous improvement and learning, and lining up testing with business objectives.